Resolution-Adaptive Source-Channel Coding for End-to-End Wireless Image Transmission
Abstract
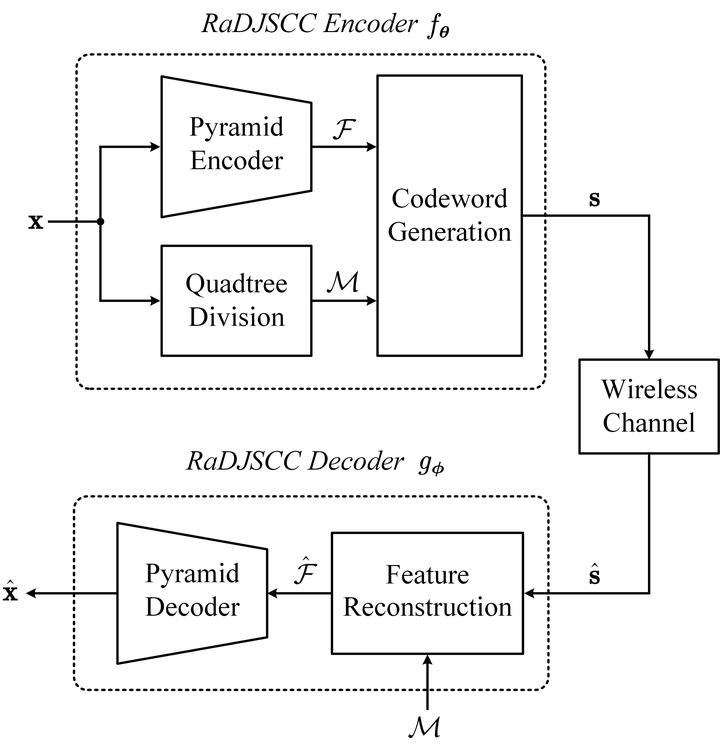
The recent deep learning-based joint source-channel coding (deep JSCC) framework has shown superior performance on end-to-end wireless image transmission without suffering from the “cliff effect”. However, a fundamental limit of current deep JSCC schemes is that the unbalanced regional importance of the source image has not been explicitly taken into account. It evenly distributes the coding rate to every image patch leading to an evident degradation of the overall coding efficiency. To break this fundamental limit, we propose a novel end-to-end wireless image transmission scheme in this paper. Our scheme integrates the deep JSCC architecture and the quadtree-structured regional rate allocation strategy adopted in the HEVC standard, collected under the name “resolution-adaptive deep JSCC (RaDJSCC)”. Our new architecture perceives the content of the transmitted image and adaptively allocates more channel bandwidth to the complex pixel blocks. Results show that for high-resolution images, the proposed RaDJSCC transmission method generally outperforms the emerging analog transmission schemes using deep JSCC and the digital transmission schemes using classical separated source and channel coding, e.g., BPG + LDPC.